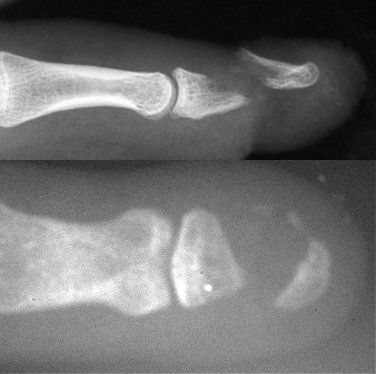

Figure Legend: Distal phalanx nonunions
are uncommon, and usually follow open injuries. Risk factors include inadequate
reduction of displaced fragments, soft tissue interposition or bone loss,
including bone loss due to surgical debridement. The top image shows the
type of acute displaced fracture which is best treated with internal fixation.
The bottom image shows an established nonunion following bone debridement
and wound closure. Most fractures which require bone debridement would
benefit from internal fixation. Late salvage of distal phalanx nonunions
is technically demanding and requires precision bone grafting technique.
| e-Hand | Go Back | Search | Textbook |